How To Read Json Data In Python

Welcome! If you want to learn how to work with JSON files in Python, and so this commodity is for you.
You volition learn:
- Why the JSON format is so important.
- Its basic construction and information types.
- How JSON and Python Dictionaries work together in Python.
- How to work with the Python congenital-in
jsonmodule. - How to convert JSON strings to Python objects and vice versa.
- How to employ
loads()anddumps() - How to indent JSON strings automatically.
- How to read JSON files in Python using
load() - How to write to JSON files in Python using
dump() - And more!
Are you ready? Let's brainstorm! ✨
🔹 Introduction: What is JSON?

The JSON format was originally inspired by the syntax of JavaScript (a programming linguistic communication used for web development). Merely since and so it has become a language-independent information format and most of the programming languages that we utilize today can generate and read JSON.
Importance and Use Cases of JSON
JSON is basically a format used to store or represent data. Its common utilise cases include spider web evolution and configuration files.
Let'south see why:
- Web Development: JSON is commonly used to transport data from the server to the client and vice versa in web applications.
- Configuration files: JSON is besides used to store configurations and settings. For example, to create a Google Chrome App, yous need to include a JSON file called
manifest.jsonto specify the proper noun of the app, its description, electric current version, and other backdrop and settings.

🔸 JSON Structure and Format
Now that yous know what the JSON format is used for, let'due south see its bones structure with an example that represents the information of a pizza order:
{ "size": "medium", "cost": fifteen.67, "toppings": ["mushrooms", "pepperoni", "basil"], "extra_cheese": false, "delivery": true, "customer": { "name": "Jane Doe", "phone": aught, "email": "janedoe@e-mail.com" } } These are the principal characteristics of the JSON format:
- There is a sequence of primal-value pairs surrounded by curly brackets
{}. - Each key is mapped to a particular value using this format:
"primal": <value> 💡 Tip: The values that require quotes accept to be surrounded by double quotes.
- Key-value pairs are separated by a comma. Only the terminal pair is not followed by a comma.
{ "size": "medium", # Comma! "cost": xv.67 } 💡 Tip: We typically format JSON with dissimilar levels of indentation to make the data easier to read. In this article, you will learn how to add the indentation automatically with Python.
JSON Data Types: Keys and Values
JSON files have specific rules that decide which data types are valid for keys and values.
- Keys must be strings.
- Values tin can exist either a cord, a number, an assortment, a boolean value (
true/simulated),null, or a JSON object.
According to the Python Documentation:
Keys in central/value pairs of JSON are always of the type str. When a dictionary is converted into JSON, all the keys of the lexicon are coerced to strings. Style Guide
Co-ordinate to the Google JSON Style Guide:
- Always cull meaningful names.
- Array types should take plural key names. All other key names should be singular. For example: use
"orders"instead of"social club"if the respective value is an array. - At that place should be no comments in JSON objects.
🔹 JSON vs. Python Dictionaries
JSON and Dictionaries might await very similar at first (visually), merely they are quite different. Let's meet how they are "connected" and how they complement each other to make Python a powerful tool to piece of work with JSON files.
JSON is a file format used to stand for and shop data whereas a Python Lexicon is the bodily data structure (object) that is kept in memory while a Python programme runs.
How JSON and Python Dictionaries Piece of work Together

When we piece of work with JSON files in Python, we can't just read them and utilise the data in our program direct. This is because the entire file would be represented as a unmarried cord and we would not be able to access the key-value pairs individually.
Unless...
We use the fundamental-value pairs of the JSON file to create a Python dictionary that we can utilise in our program to read the data, apply it, and modify it (if needed).
This is the primary connectedness between JSON and Python Dictionaries. JSON is the string representation of the data and dictionaries are the actual data structures in memory that are created when the program runs.
Dandy. At present that you know more nigh JSON, let'southward start diving into the applied aspects of how y'all can work with JSON in Python.
🔸 The JSON Module
Luckily for us, Python comes with a built-in module chosen json. Information technology is installed automatically when y'all install Python and it includes functions to help you work with JSON files and strings.
We will apply this module in the coming examples.
How to Import the JSON Module
To employ json in our program, we just need to write an import statement at the top of the file.
Like this:
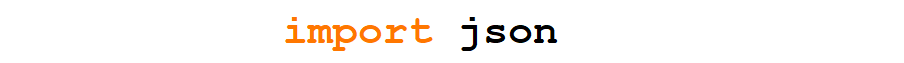
With this line, y'all volition have access to the functions defined in the module. We will use several of them in the examples.
💡 Tip: If you write this import statement, you will demand to apply this syntax to call a function defined in the json module:

🔹 Python and JSON Strings
To illustrate how some of the about important functions of the json module work, we will use a multi-line string with JSON format.
JSON String
Particularly, we will utilise this string in the examples. It is simply a regular multi-line Python string that follows the JSON format.
data_JSON = """ { "size": "Medium", "price": 15.67, "toppings": ["Mushrooms", "Actress Cheese", "Pepperoni", "Basil"], "client": { "proper noun": "Jane Doe", "phone": "455-344-234", "email": "janedoe@email.com" } } """ - To define a multi-line cord in Python, nosotros apply triple quotes.
- Then, nosotros assign the string to the variable
data_JSON.
💡 Tip: The Python Style Guide recommends using double quote characters for triple-quoted strings.
JSON String to Python Lexicon
We will use the string with JSON format to create a Python dictionary that we can admission, work with, and modify.
To do this, we will use the loads() role of the json module, passing the string as the argument.
This is the basic syntax:
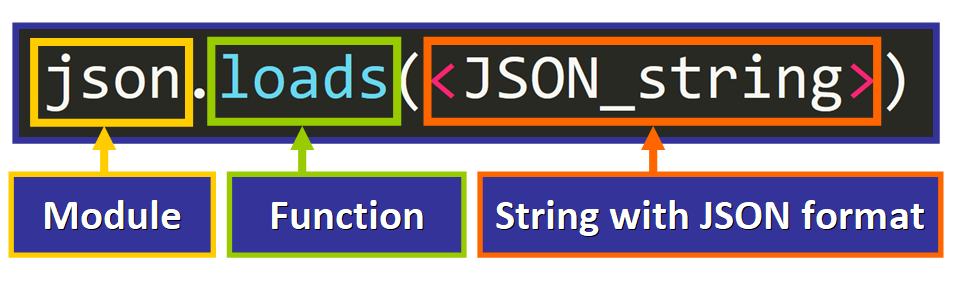
Here is the code:
# Import the module import json # Cord with JSON format data_JSON = """ { "size": "Medium", "price": xv.67, "toppings": ["Mushrooms", "Extra Cheese", "Pepperoni", "Basil"], "client": { "name": "Jane Doe", "telephone": "455-344-234", "electronic mail": "janedoe@email.com" } } """ # Catechumen JSON string to dictionary data_dict = json.loads(data_JSON) Permit's focus on this line:
data_dict = json.loads(data_JSON) -
json.loads(data_JSON)creates a new lexicon with the key-value pairs of the JSON string and it returns this new dictionary. - So, the dictionary returned is assigned to the variable
data_dict.
Awesome! If we print this dictionary, we encounter this output:
{'size': 'Medium', 'toll': 15.67, 'toppings': ['Mushrooms', 'Actress Cheese', 'Pepperoni', 'Basil'], 'customer': {'name': 'Jane Doe', 'phone': '455-344-234', 'email': 'janedoe@email.com'}} The dictionary has been populated with the information of the JSON string. Each primal-value pair was added successfully.
Now permit's see what happens when we try to access the values of the primal-value pairs with the aforementioned syntax that nosotros would employ to admission the values of a regular Python dictionary:
print(data_dict["size"]) print(data_dict["cost"]) impress(data_dict["toppings"]) impress(data_dict["client"]) The output is:
Medium 15.67 ['Mushrooms', 'Extra Cheese', 'Pepperoni', 'Basil'] {'name': 'Jane Doe', 'phone': '455-344-234', 'electronic mail': 'janedoe@email.com'} Exactly what we expected. Each key can be used to access its corresponding value.
💡 Tip: We tin utilise this dictionary just like any other Python dictionary. For example, we can call dictionary methods, add, update, and remove key-value pairs, and more. Nosotros can even utilize it in a for loop.
JSON to Python: Type Conversion
When you use loads() to create a Python dictionary from a JSON string, you volition detect that some values volition be converted into their corresponding Python values and data types.
This table presented in the Python Documentation for the json module summarizes the correspondence from JSON data types and values to Python data types and values:
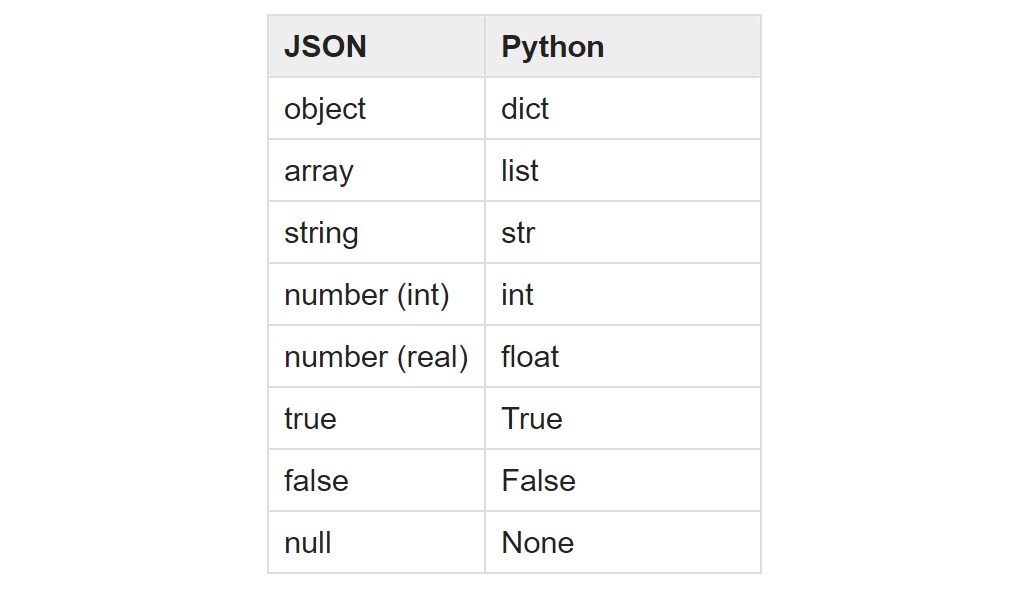
💡 Tip: The same conversion tabular array applies when we work with JSON files.
Python Lexicon to JSON String
At present you lot know how to create a Python lexicon from a string with JSON format.
Simply sometimes we might need to exercise exactly the opposite, creating a string with JSON format from an object (for example, a dictionary) to impress information technology, display information technology, store information technology, or work with information technology as a string.
To do that, we can utilise the dumps role of the json module, passing the object as argument:
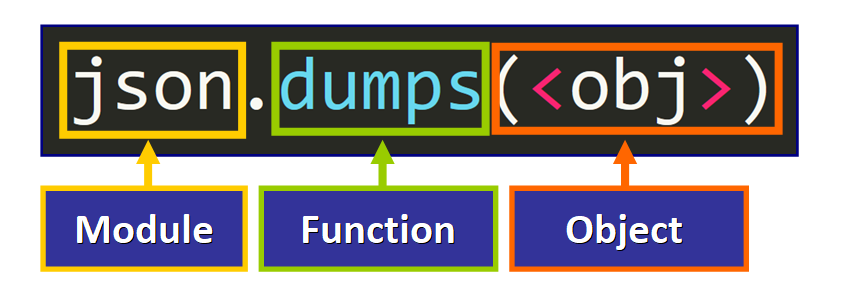
💡 Tip: This function volition render a string.
This is an example where we convert the Python dictionary client into a cord with JSON format and store it in a variable:
# Python Dictionary customer = { "name": "Nora", "age": 56, "id": "45355", "eye_color": "green", "wears_glasses": Fake } # Become a JSON formatted string client_JSON = json.dumps(client) Permit's focus on this line:
client_JSON = json.dumps(customer) -
json.dumps(client)creates and returns a string with all the key-value pairs of the dictionary in JSON format. - And so, this string is assigned to the
client_JSONvariable.
If we print this string, nosotros run into this output:
{"name": "Nora", "age": 56, "id": "45355", "eye_color": "green", "wears_glasses": false} 💡 Tip: Find that the terminal value (false) was inverse. In the Python dictionary, this value was False just in JSON, the equivalent value is false. This helps the states confirm that, indeed, the original lexicon is at present represented every bit a string with JSON format.
If nosotros check the information type of this variable, nosotros run across:
<class 'str'> So the render value of this function was definitely a string.
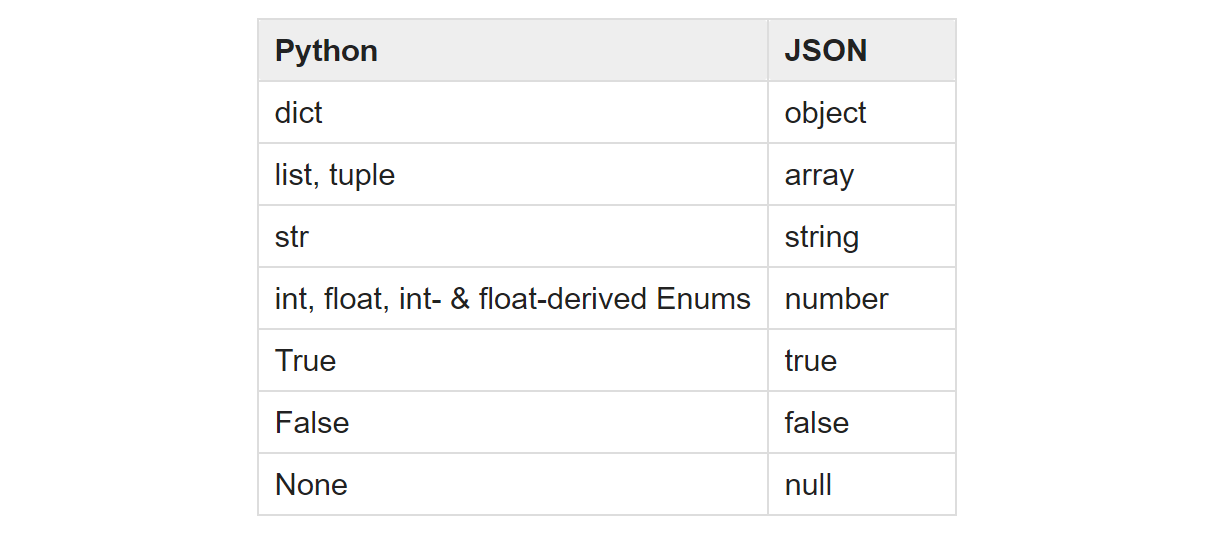
Python to JSON: Type Conversion
A process of blazon conversion occurs too when we catechumen a dictionary into a JSON cord. This table from the Python Documentation illustrates the corresponding values:
How to Impress JSON With Indentation
If we utilize the dumps part and we print the string that we got in the previous example, we run into:
{"proper noun": "Nora", "historic period": 56, "id": "45355", "eye_color": "green", "wears_glasses": false} But this is not very readable, right?
Nosotros can better the readability of the JSON cord by adding indentation.
To do this automatically, we just need to pass a second statement to specify the number of spaces that we want to employ to indent the JSON string:
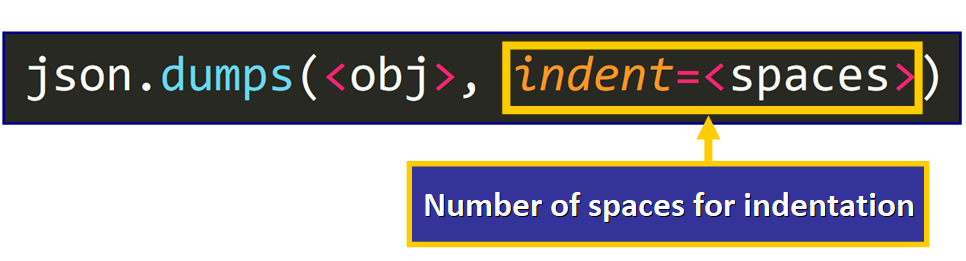
💡 Tip: the second argument has to be a non-negative integer (number of spaces) or a string. If indent is a string (such as "\t"), that string is used to indent each level (source).
Now, if nosotros call dumps with this second argument:
client_JSON = json.dumps(client, indent=4) The result of printing client_JSON is:
{ "proper noun": "Nora", "historic period": 56, "id": "45355", "eye_color": "light-green", "wears_glasses": faux } That's keen, correct? Now our cord is nicely formatted. This volition be very helpful when we start working with files to shop the data in a human-readable format.
How to Sort the Keys
Y'all can also sort the keys in alphabetical club if y'all demand to. To do this, you simply need to write the name of the parameter sort_keys and pass the value Truthful:

💡 Tip: The value of sort_keys is False by default if you don't laissez passer a value.
For example:
client_JSON = json.dumps(client, sort_keys=True) Returns this string with the keys sorted in alphabetical order:
{"age": 56, "eye_color": "green", "id": "45355", "name": "Nora", "wears_glasses": false} How to Sort Alphabetically and Indent (at the same time)
To generate a JSON string that is sorted alphabetically and indented, you just demand to laissez passer the two arguments:

In this example, the output is:
{ "age": 56, "eye_color": "light-green", "id": "45355", "proper name": "Nora", "wears_glasses": false } 💡 Tip: You lot can laissez passer these arguments in any order (relative to each other), simply the object has to exist the first argument in the list.
Bang-up. Now you know how to piece of work with JSON strings, so allow'due south see how you lot tin work with JSON files in your Python programs.
🔸 JSON and Files
Typically, JSON is used to store data in files, and so Python gives usa the tools nosotros demand to read these types of file in our program, work with their information, and write new information.
💡 Tip: a JSON file has a .json extension:
Let's meet how we tin can work with .json files in Python.
How to Read a JSON File in Python
Let's say that nosotros created an orders.json file with this data that represents 2 orders in a pizza shop:
{ "orders": [ { "size": "medium", "price": 15.67, "toppings": ["mushrooms", "pepperoni", "basil"], "extra_cheese": false, "delivery": truthful, "client": { "name": "Jane Doe", "phone": goose egg, "email": "janedoe@electronic mail.com" } }, { "size": "small-scale", "toll": six.54, "toppings": null, "extra_cheese": truthful, "delivery": false, "customer": { "name": "Foo Jones", "phone": "556-342-452", "email": null } } ] } Please take a moment to clarify the construction of this JSON file.
Here are some quick tips:
- Notice the information types of the values, the indentation, and the overall structure of the file.
- The value of the primary cardinal
"orders"is an array of JSON objects (this array will be represented as list in Python). Each JSON object holds the data of a pizza order.
If nosotros want to read this file in Python, we just need to use a with statement:
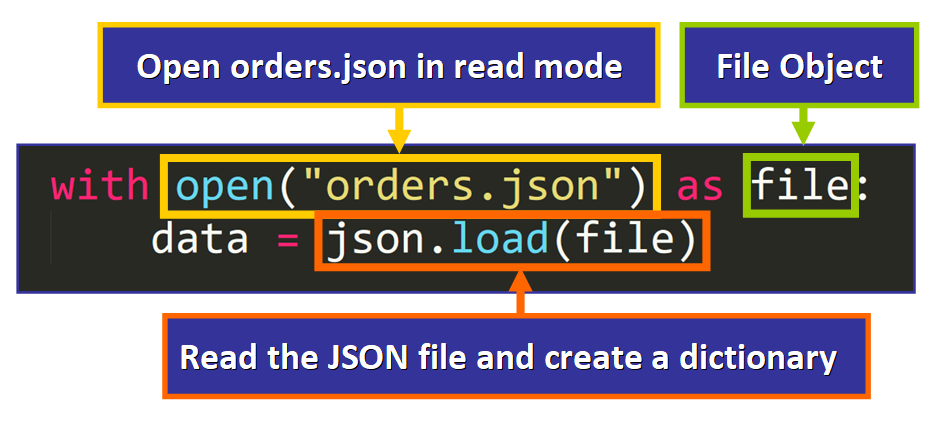
💡 Tip: In the syntax higher up, we can assign any name to file (green box). This is a variable that nosotros can use within the with statement to refer to the file object.
The fundamental line of lawmaking in this syntax is:
information = json.load(file) -
json.load(file)creates and returns a new Python dictionary with the primal-value pairs in the JSON file. - Then, this dictionary is assigned to the
datavariable.
💡 Tip: Notice that nosotros are using load() instead of loads(). This is a unlike office in the json module. Yous will learn more nigh their differences at the end of this article.
Once nosotros have the content of the JSON file stored in the data variable every bit a dictionary, we tin can employ it to exercise basically anything nosotros want.
Examples
For example, if nosotros write:
print(len(data["orders"])) The output is ii because the value of the main primal "orders" is a listing with two elements.
We can likewise utilise the keys to access their corresponding values. This is what we typically do when nosotros piece of work with JSON files.
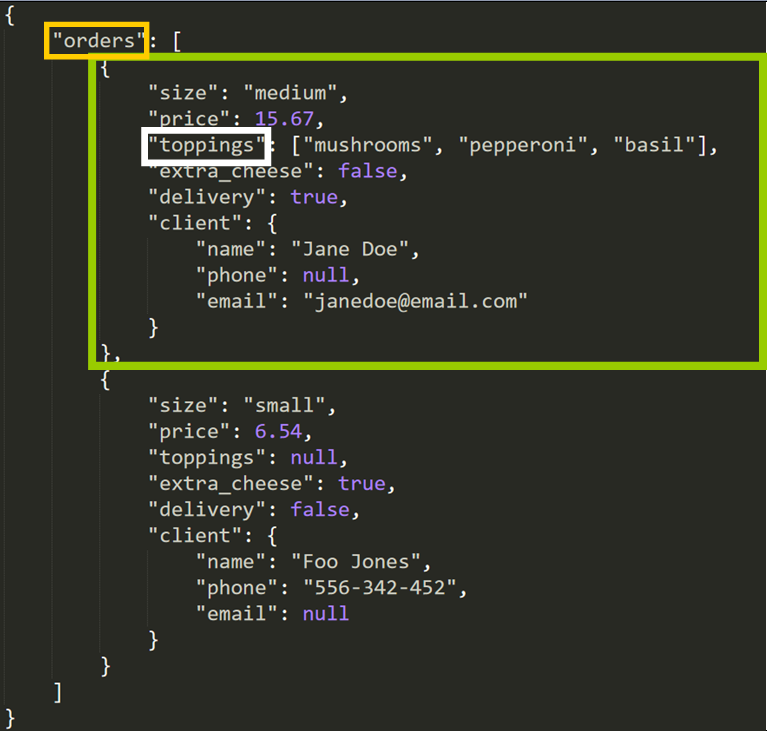
For example, to admission the toppings of the beginning social club, we would write:
information["orders"][0]["toppings"] - Start, we select the main key
"orders" - So, we select the first element in the list (index
0). - Finally, we select the value that corresponds to the key
"toppings"
You can see this "path" graphically in the diagram:
If we impress this value, the output is:
['mushrooms', 'pepperoni', 'basil'] Exactly what we expected. You merely demand to "swoop deeper" into the structure of the dictionary by using the necessary keys and indices. You can use the original JSON file/string as a visual reference. This manner, yous tin access, modify, or delete any value.
💡 Tip: Remember that we are working with the new dictionary. The changes made to this lexicon will non bear on the JSON file. To update the content of the file, we need to write to the file.
How to Write to a JSON File
Let'due south see how you tin can write to a JSON file.
The first line of the with statement is very similar. The only change is that you need to open the file in 'due west' (write) style to be able to modify the file.

💡 Tip: If the file doesn't exist already in the current working directory (folder), it will exist created automatically. Past using the 'w' fashion, nosotros will exist replacing the unabridged content of the file if it already exists.
There are 2 alternative ways to write to a JSON file in the body of the with argument:
-
dump -
dumps
Let's see them in detail.
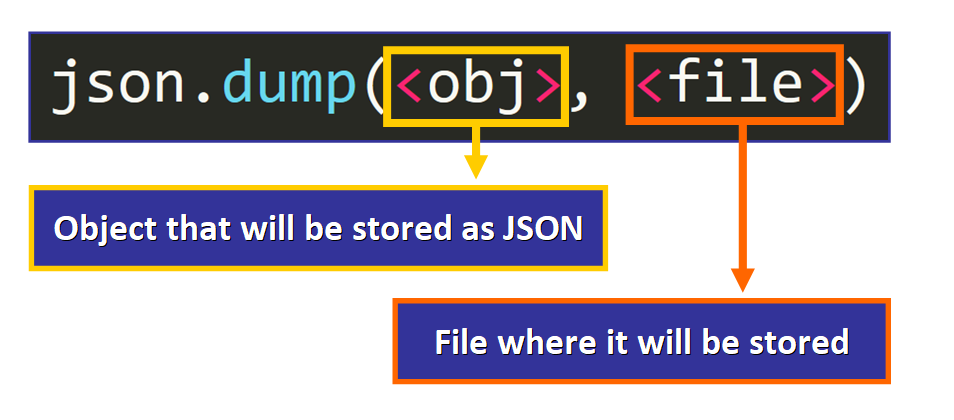
Get-go Approach: dump
This is a function that takes two arguments:
- The object that will be stored in JSON format (for example, a dictionary).
- The file where information technology will be stored (a file object).
Permit's say that the pizza shop wants to remove the clients' data from the JSON file and create a new JSON file called orders_new.json with this new version.
We tin practice this with this code:
# Open the orders.json file with open up("orders.json") as file: # Load its content and make a new dictionary data = json.load(file) # Delete the "client" cardinal-value pair from each social club for society in data["orders"]: del guild["client"] # Open up (or create) an orders_new.json file # and store the new version of the data. with open("orders_new.json", 'due west') as file: json.dump(data, file) This was the original version of the data in the orders.json file. Notice that the "client" key-value pair exists.
{ "orders": [ { "size": "medium", "price": 15.67, "toppings": ["mushrooms", "pepperoni", "basil"], "extra_cheese": false, "delivery": true, "client": { "name": "Jane Doe", "phone": naught, "email": "janedoe@email.com" } }, { "size": "small-scale", "price": 6.54, "toppings": null, "extra_cheese": true, "delivery": false, "customer": { "proper noun": "Foo Jones", "phone": "556-342-452", "email": null } } ] } This is the new version in the orders_new.json file:
{"orders": [{"size": "medium", "cost": 15.67, "toppings": ["mushrooms", "pepperoni", "basil"], "extra_cheese": faux, "delivery": true}, {"size": "small", "price": 6.54, "toppings": null, "extra_cheese": truthful, "delivery": false}]} If you analyze this carefully, yous volition run into that the "clients" key-value pair was removed from all the orders.
Withal, in that location is something missing in this file, right?
Please accept a moment to think about this... What could it be?
Indentation, of course!
The file doesn't really look like a JSON file, but nosotros can easily set this by passing the argument indentation=4 to dump().
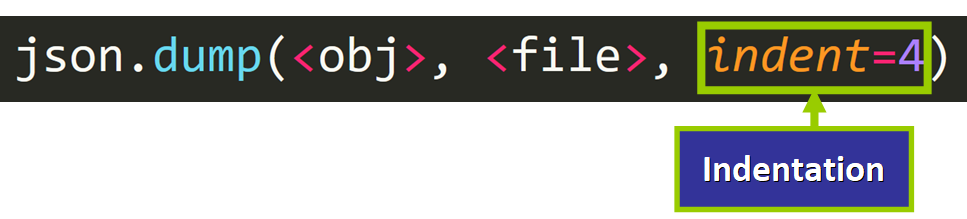
Now the content of the file looks similar this:
{ "orders": [ { "size": "medium", "price": xv.67, "toppings": [ "mushrooms", "pepperoni", "basil" ], "extra_cheese": fake, "delivery": true }, { "size": "small", "price": 6.54, "toppings": null, "extra_cheese": true, "delivery": faux } ] } What a difference! This is exactly what we would wait a JSON file to look similar.
Now you lot know how to read and write to JSON files using load() and dump(). Let'due south encounter the differences between these functions and the functions that we used to piece of work with JSON strings.
🔹 load() vs. loads()
This table summarizes the key differences between these ii functions:
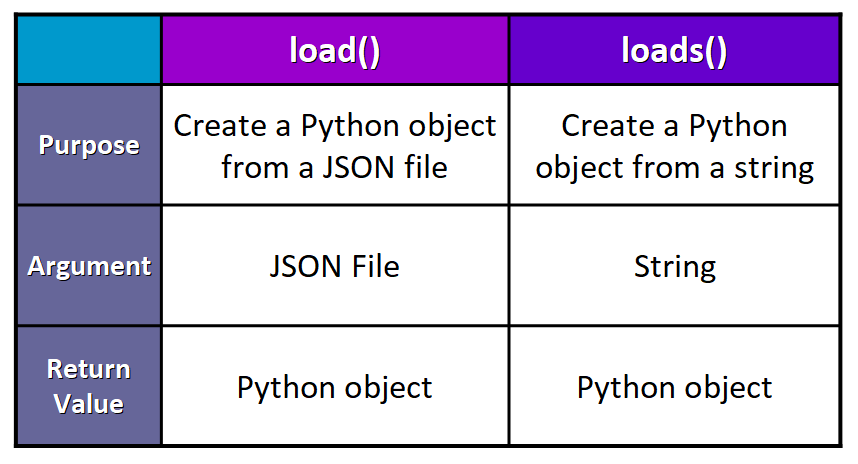
💡 Tip: Think of loads() as "load string" and that volition help you remember which function is used for which purpose.
🔸 dump() vs. dumps()
Here nosotros accept a table that summarizes the key differences between these ii functions:
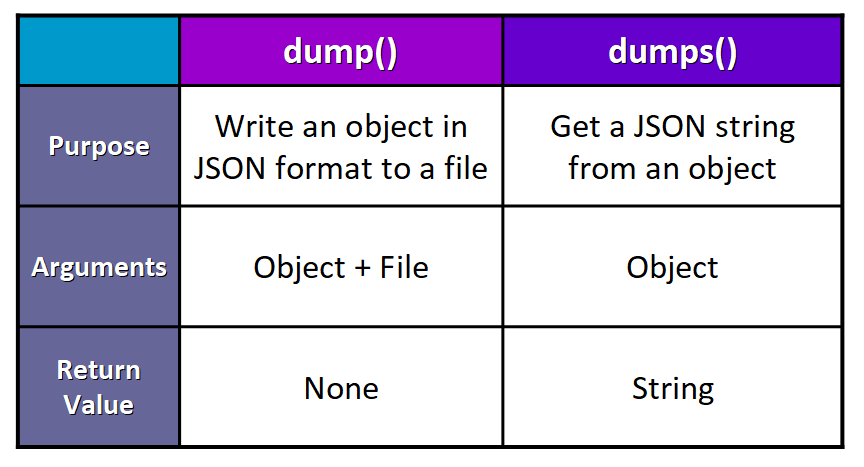
💡 Tip: Think of dumps() equally a "dump string" and that will help you remember which function is used for which purpose.
🔹 Important Terminology in JSON
Finally, there are ii important terms that you need to know to piece of work with JSON:
- Serialization: converting an object into a JSON string.
- Deserialization: converting a JSON string into an object.
🔸 In Summary
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a format used to represent and store data.
- It is commonly used to transfer data on the web and to store configuration settings.
- JSON files have a
.jsonextension. - You can catechumen JSON strings into Python objects and vice versa.
- You can read JSON files and create Python objects from their key-value pairs.
- Y'all tin write to JSON files to store the content of Python objects in JSON format.
I actually hope you liked my article and institute it helpful. Now you know how to piece of work with JSON in Python. Follow me on Twitter @EstefaniaCassN and cheque out my online courses.
Larn to lawmaking for free. freeCodeCamp'due south open source curriculum has helped more 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
How To Read Json Data In Python,
Source: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-read-json-file-how-to-load-json-from-a-file-and-parse-dumps/
Posted by: sotocapts1955.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Read Json Data In Python"
Post a Comment